1.2 Program Function and Purpose
Notes on program function
1.2 Daily Video 1
Learning Objectives:
- Describe the purpose of a computing innovation
Computing Innovations
- The purpose of computing innovations is to solve prpoblems or to pursue interests through creative expression
- Categories of innovations
- Applications
- Games
- Social media
- Business
- Productivity
- Physical devices
- Computers
- Smartphones/tablets
- Wearables
- Systems
- E-commerce
- Cloud services
- Applications
Innovations created for a purpose
- An understanding of the purpose of a computing innovation provides developers with an improved ability to develop that computing innovation
- When thinking about innovations created for a purpose, think about the guiding questions:
- Why does the computing innovation exist?
- What problems does the computing innovation solve?
- What does the computing innovation allow us to do that we could not do before?
Examples of Computing Innovations
- Social media applications
- Allows users to connect from a distance and archive their activies
- E-commerce
- Allows users to save time and money by being able to shop from home
- Digital assistant device
- Allows users to control their devices hands-free, making them safer while driving or more convenient when multitasking
1.2 Daily Video 2
Learning Objectives:
- Identify input(s) to a program
- Identify output(s) producced by a program
Identifying Inputs to Programs
- Program inputs are data sent to a computer for processing by a program
- Computer programs accept input in various forms: tactile, audio, visual, text
How do programs receive input?
-
“Events” are triggered by some action, which usually sends input to the program
- i.e. mouse clicks, screen-taps, button clicks, keyboard entries, audio triggers
- Input can come from a user or other programs
What does input accomplish in a program?
- Input usually affects the output
- Program outputs are any data sent from a program to a device
- Outputs produced by devices: visual, audio, tectile, text
How does a program know what to do upon an event?
- In event-driven programming, program statements are executed when triggered, rather than through the sequential flow of control
- An action triggers an event
- Action may be initiated by the user or another program/device
- The program “jumps” to the code segment according to the event
- The code segment is executed
- Output is triggered by the code segment (or additional events)
- The program code is not necessarily executed in order
- Code segments are executed as they are called according to the events triggered
-
Program output is usually based on a program’s input or prior state
- i.e. internal values
1.2 Daily Video 3
Learning Objectives:
- Explain how a program or code segment functions
What is a program?
-
A program is a collection of statements that performs a specific task when run by a computer
- A statement is a single command
- A group of statements part of a program is called a code segment
- Code segments are executed according to the rules of the programming language
- A program is often referred to as software
- The behavior of a program is how a program functions during execution and is often descirbed by how a user interacts with it
Program Function
-
A program needs to work for a variety of inputs and situations
- Code segment would need to work for a variety of lists
- Code segment could be inserted into a larger program
- A program can be described broadly by what it does, or in more detail by both what the program does and how the program statements accomplish this function
- Description should:
- state the function simply so someone could use the code segment in a larger program
- include how it functions by explaining in detail how the code segment functions
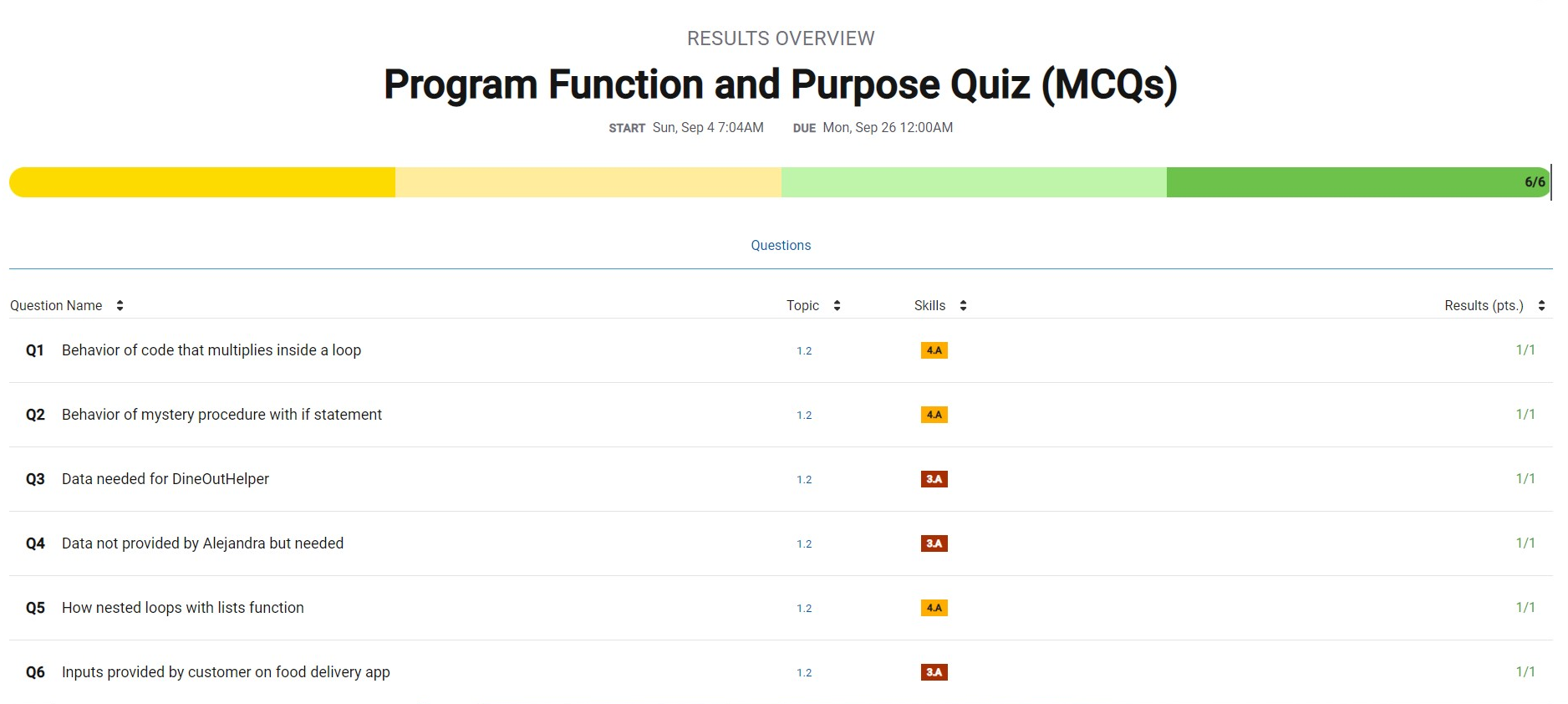
MCQ
Our Team’s Final Project
- Do we have final project ideas for a PBL Web Project?
- Yes, our team is planning to create a productive planner with many different uses.
- Are we considering a project that is best for our educational purpose?
- Yes, most of us have minimal coding experience, so by creating a not too complicated but still useful application, we will all learn a lot. We can even utilize the application ourselves after it is complete.
- Is the project going to hold team members interest for 8 weeks?
- Yes, there are many different elements to incorporate into this project. Even if we somehow complete our original plan, there is big capacity for new other elements to be implemented.
- Does the project have potential for someone to use it beyond the 8 weeks? ie Customer or Sponsor needed?
- Yes, this application is very useful and can be utilized by anyone. A planner is something everyone needs, we are just making it even more convenient and useful.
- Does the project have potential to be used for Create Performance Task submission?
- Yes, in our project there are many ways to implement code that includes sequencing, selection and iteration, procedures and lists, etc. in a functionable and creative way